Tax-Efficient Family Investing: How Discretionary Trusts Can Help Breadwinners Reduce Their Tax Burden
John is the primary breadwinner in his family, earning a significantly higher income than his spouse. While this income provides financial security for the family, it also comes with a hefty tax bill. John wants to grow his family’s wealth by investing wisely but is keen to find a way to manage the tax implications of these investments effectively. One powerful solution that can help John achieve his goals is setting up a discretionary trust. In this blog, we’ll explore how discretionary trusts can provide tax benefits for families where one member earns a significantly higher income, allowing them to maximise their investments and reduce their overall tax burden.

The Challenge: High Tax Burden on the Primary Breadwinner
As the main income earner, John finds himself in a high tax bracket, paying a large portion of his income in taxes. Any additional income generated from investments would also be taxed at this high marginal rate, reducing the potential returns that John can earn on his investments.
At the same time, John’s spouse is in a much lower tax bracket due to lower or no taxable income. This situation presents an opportunity for tax planning, as shifting some of the income to family members in lower tax brackets can reduce the overall tax burden and improve the family’s financial position.
The Solution: Using a Discretionary Trust for Tax-Efficient Investing
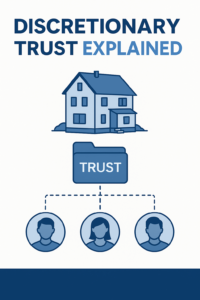
To manage taxes more effectively, John can set up a discretionary trust to hold and manage his family’s investments. Here’s how this strategy works:
- Establishing a Discretionary Trust:
John sets up a discretionary trust, which will be used to accumulate new investments. This trust acts as a separate legal entity, allowing John to direct income and capital gains away from his personal tax liability. - Income Distribution to Lower Tax Bracket Beneficiaries:
The discretionary trust can distribute any income or capital gains generated by the investments to beneficiaries of the trust, such as John’s spouse or adult children. Since these beneficiaries are in lower tax brackets, the income distributed to them will be taxed at a lower rate. This effectively spreads the tax burden across the family, reducing the total tax payable. - Flexibility in Distributions:
One of the key advantages of a discretionary trust is the flexibility it offers. The trustee has the discretion to decide how much income to distribute and to whom. This means that each year, John can adjust the income distributions based on the tax positions of the beneficiaries, optimising the family’s tax situation. If John’s spouse takes on a higher-paying job, for example, the trust can shift more income to the adult children or retain it within the trust to manage taxes efficiently.
Key Considerations: Setting Up and Managing a Discretionary Trust
While the benefits of using a discretionary trust are clear, John must consider several important factors to ensure the trust is set up and managed effectively:
- Professional Advice: Setting up a discretionary trust involves legal, tax, and administrative complexities. John should work with legal and tax advisors to ensure the trust is structured correctly, complies with all relevant regulations, and aligns with his family’s financial goals.
- Trust Deed Flexibility: The trust deed should be carefully drafted to include a broad range of potential beneficiaries. This flexibility ensures that John can adapt to changing family circumstances, such as future children, grandchildren, or other relatives who may become beneficiaries.
- Record-Keeping and Compliance: Managing a discretionary trust requires diligent record-keeping and compliance with tax laws. Proper documentation of income distributions, trustee decisions, and beneficiary details is essential to demonstrate that the trust is being used for legitimate family wealth management purposes.
- Tax Implications for Beneficiaries: While the trust can distribute income to beneficiaries in lower tax brackets, it’s important to be mindful of how this income might impact the beneficiaries’ own tax positions or eligibility for certain government benefits. John should work with his advisors to balance these considerations effectively.
The Benefits: Optimising Family Wealth Through Tax Efficiency
By using a discretionary trust, John can achieve several significant benefits:
- Reduced Tax Liability: By distributing investment income to family members in lower tax brackets, the overall tax burden on the family’s wealth is reduced. This results in more after-tax income being available for reinvestment or family use.
- Enhanced Investment Returns: Lower tax rates mean more of the investment returns are retained, allowing the family’s wealth to grow more quickly over time.
- Financial Flexibility and Security: The trust provides a flexible and controlled way to manage and distribute family wealth. This flexibility helps ensure that funds are available when needed and are allocated in a tax-efficient manner, providing long-term financial security for John’s family.
Conclusion: Leveraging Discretionary Trusts for Smart Family Investing
For families where one member earns significantly more than others, using a discretionary trust can be a powerful strategy to manage taxes and enhance wealth. By establishing a discretionary trust, John can distribute investment income to family members in lower tax brackets, reducing the overall tax burden and maximising the family’s financial resources. This approach not only provides tax savings but also supports strategic wealth management, allowing families to build and protect their financial future.
If you’re considering ways to optimise your family’s tax strategy and grow your investments, consulting with legal and financial professionals about setting up a discretionary trust is a wise step. With the right planning, you can take full advantage of the tax benefits and ensure a secure financial future for you and your loved ones.
Others
-
October 20, 2025 Buying Property Under Your Personal Name in Australia: Pros and Cons
-
October 18, 2025 Service Trust Business Structure in Australia